Do you suffer from allergic-type reactions but cannot find their cause? If so, you may have a histamine intolerance.
What is Histamine?
To better understand histamine intolerance, we first need to recognize histamine and the role it plays in our bodies. Histamine exists all around us: from the foods we eat, to animals and plants, and in our own tissue. Most of the histamine in the human body is contained in mast cells, a type of white blood cell, which play roles in not only our allergy and anaphylactic systems, but also in protective bodily responses like wound healing. In an allergic response, histamine is released from the tissue mast cells into the bloodstream and causes allergic reaction symptoms such as inflammation.
What is Histamine Intolerance?
Normally, the histamine you consume is broken down in your body through various degradation processes—but when your body can’t break down the histamine, it can result in a variety of unpleasant symptoms. The problem is called histaminosis, or histamine intolerance. Since histamine intolerance can result in a host of allergic reactions, it’s impossible to diagnose based on symptoms alone.
Rather, if you experience the symptoms below but continue to test negative for allergies, histamine intolerance might be the answer you’ve been searching for. Symptoms of histamine intolerance vary widely, and are quite inconsistent. Many are what you’d relate to an allergic reaction: sneezing, runny nose, trouble breathing, swelling and irritation, to name a few. But the list doesn’t stop there — histamine intolerance could also manifest through flu-like or even food poisoning symptoms such as heartburn, digestive problems, nausea, or hot flashes. If you have a histamine intolerance, you may experience these symptoms chronically, or after eating certain foods.
Histamine in Foods
Many foods contain histamine, but some have more histamine than others. Eliminating foods with high levels of histamine can help manage and eradicate symptoms of histamine intolerance. It’s also helpful to keep a food journal of everything that you eat—that way, if symptoms arise, you can track them back to your diet and know what triggers you. Foods with a high level of histamine tend to be processed, preserved, or pickled. Things that are fermented, like alcohol or kimchi, are especially high in histamine, as well as foods that are “matured,” like cheese and cured meats. On the other hand, foods low in histamine are fresh and haven’t been processed: fresh meats, fruits, vegetables, and pasteurized milk products tend to be low in histamine (1).
High Histamine Foods
- Alcohol
- Pickled or canned foods – sauerkrauts
- Matured cheeses
- Smoked meat products – salami, ham, sausages….
- Shellfish
- Beans and pulses – chickpeas, soy beans, peanuts
- Nuts – walnuts, cashew nuts
- Chocolates and other cocoa based products
- Vinegar
- Ready meals
- Salty snacks, sweets with preservatives and artificial colorings
Low Histamine Foods
- Fresh meat (cooled, frozen or fresh)
- Freshly caught fish
- Chicken (skinned and fresh)
- Egg yolk
- Fresh fruits – with the exception of strawberries, most fresh fruits are considered to have a low histamine level (also see histamine liberators below)
- Fresh vegetables – with the exception of tomatoes
- Grains – rice noodles, yeast free rye bread, rice crisp bread, oats, puffed rice crackers, millet flour, pasta (spelt and corn based)
- Fresh pasteurised milk and milk products
- Milk substitutes – coconut milk, rice milk
- Cream cheese, butter (without the histamine generating rancidity)
- Most cooking oils – check suitability before use
- Most leafy herbs – check suitability before use
- Most non-citric fruit juices
- Some Herbal teas
Diagnosing Histamine Intolerance
Histamine intolerance, as previously noted, is difficult to diagnose. Some diagnoses happen through process of elimination, or differential diagnosis. In a differential diagnosis, a doctor would first test for allergies and possible food sensitivities such as Celiac disease. If a differential diagnosis does not uncover a certain allergy or sensitivity, then your doctor can begin to directly test for histamine intolerance. Because histamine intolerance is the result of a lack of specific enzymes in your body to metabolize histamine (diamine oxidase), your doctor can test your levels of histamine and diamine oxidase before and after a low-histamine food regimen.
Treating Histamine Intolerance
If you and your doctor have determined that you suffer from a histamine tolerance, have no fear! Histamine intolerance is not permanent, and there are a few simple steps you can take to minimize your symptoms and feel healthy again. The first step you can take is modifying your diet so as to reduce your histamine intake. Eat fresh foods wherever you can, and avoid anything processed, cured, pickled, or fermented. After that, ask your doctor what supplements he or she recommends for treatment: depending on individual factors, they may recommend certain vitamins, antihistamines, or even a diamine oxidase supplement. Navigating your path through and beyond histamine intolerance is not simple, but there are many resources and directives in place to demystify the condition and make it easy for you to live your life symptom-free.
Fill out the from below or call Tringali Vibrant Health today to book a consultation and get to the bottom or your symptoms today: 561-283-1166.
Our Favorite Histamine Supplement:
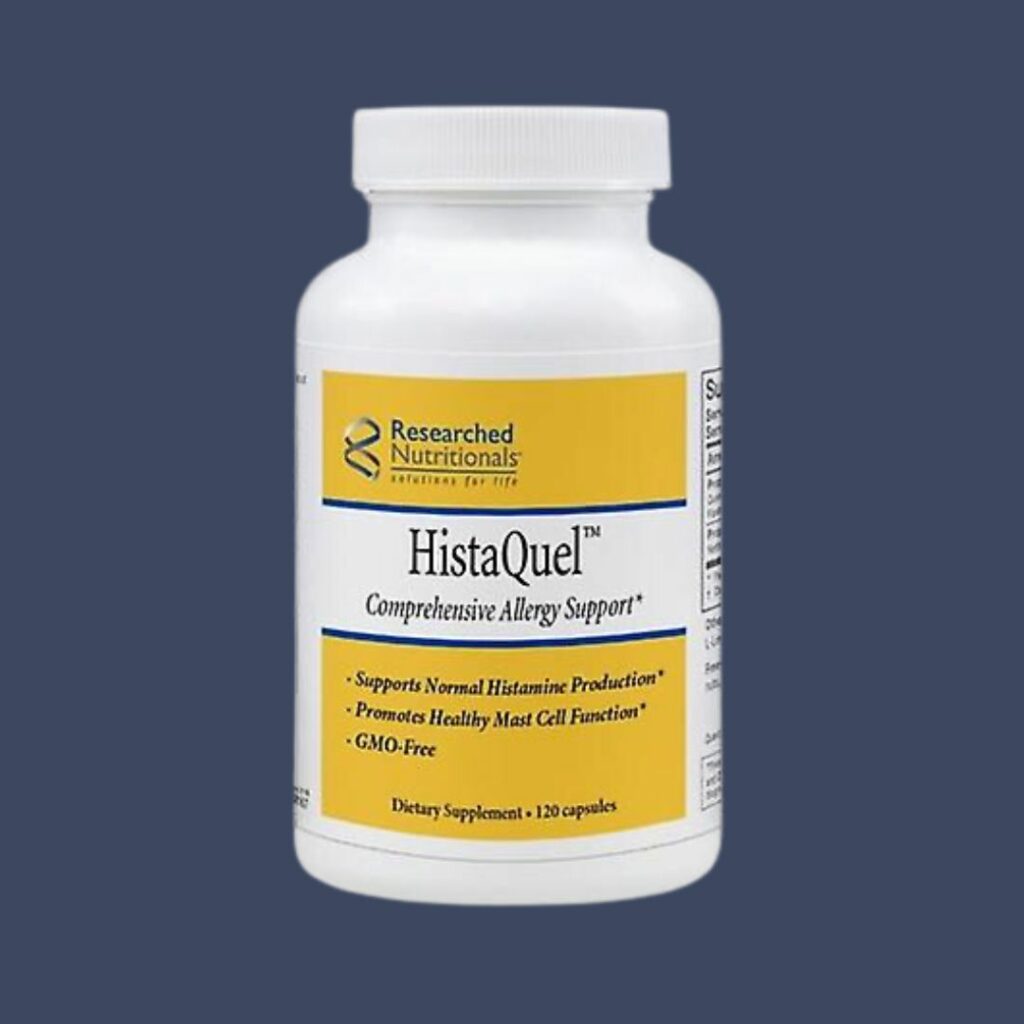
HistaQuel® – Comprehensive Mast Cell Support*
HistaQuel® is a comprehensive formula providing a multi-faceted, systemic approach to supporting healthy mast cell function and histamine response*